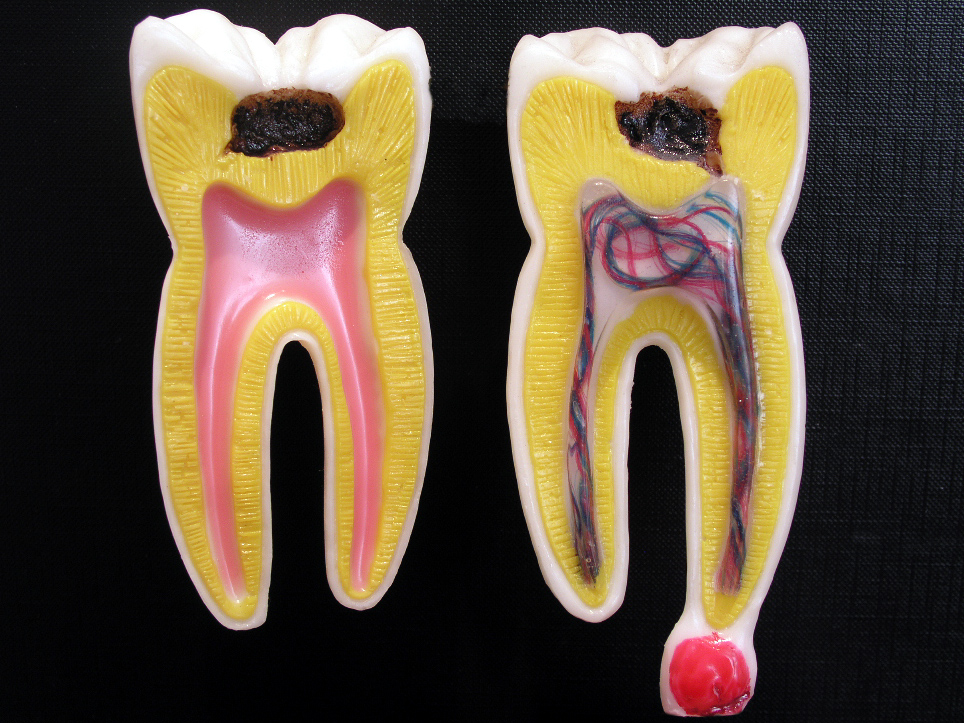
While having a toothache is never any fun, dismissing it as “not that big of a deal” could be a big mistake. This is because the pain you are feeling could be a warning sign of pulpitis.
What Is Pulpitis?
Pulpitis occurs when a bacterial infection spreads to the pulp chamber of an infected tooth, causing tissue to become swollen, inflamed or irritated deep inside the affected tooth. Pain is caused because the infection puts pressure on the surrounding nerves, blood vessels and tissue inside the tooth.
There are two main types of pulpitis, reversible and irreversible. Generally, the pain level of reversible pulpitis is slight while irreversible pulpitis features more severe pain.
Reversible Pulpitis
Reversible pulpitis happens when the pain and discomfort from an infected tooth dissipates after treatment of inflamed areas. This procedure usually involves clearing out the affected region and getting a filling. However, if unchecked, the pulp inside the chamber could become severely infected or die, causing irreversible damage to the tooth.
Irreversible Pulpitis
By contrast, irreversible pulpitis is much more painful and severe. This usually transpires because the pulp tissue starts to decay after the blood flowing to that part of the tooth is cut off by inflammation. The situation could worsen If the immune system becomes overwhelmed and cannot break down the excess dead tissue. This increases the risk of an abscess forming, which could worsen if the infection spreads to nearby bones and throughout the body.
Once irreversible pulpitis is diagnosed, an endodontist will often perform a root canal to clear out the dead pulp and help alleviate pain. Another option, although not a preferred one, is tooth extraction. This usually happens because of an injury, dental infection or because dental pulp necrosis has set in.
When irreversible pulpitis reaches its final stage, the nerve endings that connect to the soft pulp inside the tooth has completely died. As a result there are no feelings in the tooth. Patients will often notice discoloration of the affected tooth.. This process is referred to as dental pulp necrosis.
If not treated, dental pulp necrosis could cause further health issues, including additional tooth decay, abccesses, sinusitis, bone loss in the jaw, and gum disease.
Symptoms of Pulpitis
In most instances, reversible and irreversible pulpitis share the common symptoms of puffiness and a feeling of pressure around the infected tooth. Infected teeth are also sensitive
to sugary foods and hot and cold temperatures.
With both forms, the infected tooth feels painful and inflamed. However, the soreness and tenderness caused by reversible pulpitis is milder and often occurs only while chewing or eating. Likewise, the pain associated with irreversible pulpitis is more of a throbbing or ongoing ache that runs throughout the infected tooth.
Patients should also be aware of several other symptoms of irreversible pulpitis. These include infection, swollen lymph nodes, fever, bad breath, sensitivity to temperature changes, and an unpleasant taste in the mouth. It can also feature the formation of pockets of pus which are caused as the infection spreads beyond the affected tooth.
It is important to note that these same symptoms can also be caused by other oral health issues, such as halitosis, poor dental hygiene, or cavities. Dental procedures like deep cleaning can also cause a reaction to hot and cold temperatures. Swelling and pain could also be associated with chipped or fractured teeth, dental fillings, and root canals. This is why you should have your diagnosis verified by a professional if you are noticing any of the warning signs.
How Is Pulpitis Diagnosed?
The best was to diagnose pulpitis is visit your dentist as soon as pain begins. Once your dentist has given you a physical examination to determine the severity of your condition so an appropriate treatment can be applied. This is important, because the longer you wait, the longer and more intense treatment will have to be.
Thankfully, modern technology has given dentists multiple tools for diagnosing and treating pulpitis. This includes X-Rays and digital imaging which gives allows them to scan the infected tooth to determine whether the patient is suffering from it, or another condition. It also allows them to see if the infection has spread to other areas.
Because determining if the core of a tooth is healthy, infected or necrotic is important, dentists will often use a pulp vitality tester, an electric device that reveals if the pulp inside the chamber is still alive. This is done by sending an electric current to the appropriate tooth to measure how it responds to the charge. If there is a reaction then dental pulp necrosis has yet to set in.
Another method for diagnosis involves determining how the infected tooth responds to cold and warm temperatures. This will also allow dentists to evaluate the extent of decay before proceeding to treatment. If irreversible pulpitis is detected your dentist may refer you to an endodontist.
Is Pulpitis Dangerous?
Pulpitis can be dangerous if left untreated. This is because it can quickly spread infection to other parts of the body, leading to other medical complications.
Here are some situations where Pulpitis could be dangerous.
- Living in a region without adequate access to fluoridated water poses a much higher risk of danger because there is an increased threat of exposure to threatening bacteria.
- Several medical conditions, including Meningitis, HIV and Diabetes can increase the risk of pulpitis.
- Negligent care and poor oral hygiene are other possible causes for reversible and irreversible pulpitis.
Another way to avoid the harmful effects of pulpitis is to practice healthy eating. This includes avoiding a diet that is high in sugars while also eliminating soft drinks and candy sweets. Doing this will help eliminate tooth decay and prevent issues that may require root canals or the extraction of an infected tooth.
The formation of an abscess from untreated pulpitis is also very dangerous because, in addition to affecting the bone surrounding the infected tooth, it could cause swelling in the face, neck and throat that could make breathing difficult.
Since there are many side effects from pulpitis those suffering from toothaches and oral soreness are encouraged to seek the help of a dentist immediately. Use our online search tool to find someone near you.